As the business grows, many companies use external partners to manage their warehouses, transportation, and fulfillment. This is a fundamental reason why understanding 3PLvs. 4PL models is crucial today. In Australia, the logistics outsourcing market continues to grow, with the 3PL sector predicted to grow by USD 44.32 billion by 2033, with a CAGR from 2025 at an increase of 7.04% in 2025. This rise in demand highlights the importance of outsourced logistics to modern supply chains when evaluating 4PLvs 3PL options.
What is 3PL? (Third-Party Logistics Explained)
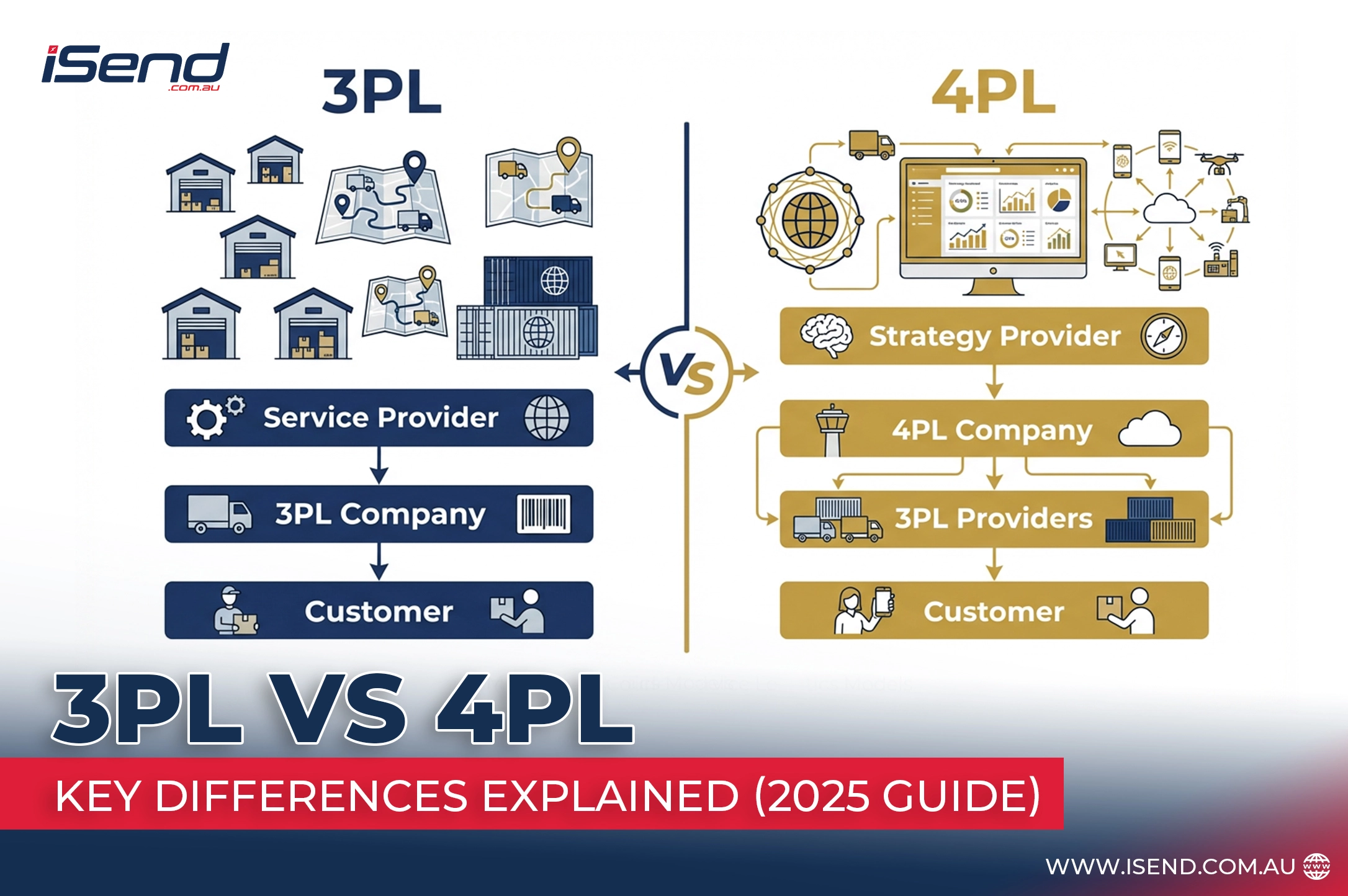
It refers to the outsourcing of the logistics operations to a specialized external provider. These suppliers handle operational components such as order fulfillment, stock management, packaging, picking, warehousing, and transportation. Most 3PLs operate dedicated fulfillment centers equipped with a Warehouse Management System (WMS), barcode scanning equipment, automated sorting belts, and carrier integrations with other companies, such as DHL, FedEx, and Australia Post. The 3PLs enable companies to save on storage expenses, enhance delivery speed, and have real-time supply chain visibility.
Who should use 3PL?
E-commerce businesses, manufacturers, and retailers utilize 3PL services to enhance their operational efficiency and concentrate on core business activities. The features of 3PL providers:
● Manage distribution, warehousing and shipping
● Provide freight forwarding and clearance
● offer inventory control applications (real-time stock, prediction)
● Automate pick-pack to make order fulfillment services possible
● integrate e-commerce networks with the marketplaces like Shopify, Amazon, eBay, WooCommerce, and many more.
What is 4PL? (Fourth-Party Logistics Explained)
A Lead Logistics Provider (LLP), or fourth-party logistics (4PL), is an extension of the operational practice of 3PLs. A 4PL is a supply chain partner that manages all logistics ecosystem components and coordinates them. It manages end-to-end planning, technology, vendor relationships, and multi-3PL functions. It acts as a single point of contact for the business. This makes 4PL suitable for an organization where complete supply chain control and long-term optimization are required.
When do businesses choose 4PL?
It provides a comprehensive solution:
Strategic Planning:
To design an optimized logistics strategy, a 4PL analyzes demand patterns, supplier performance, transportation costs, and warehouse productivity. This involves network redesign, vendor selection, route planning, forecasting, and performance benchmarking to increase responsiveness and cost savings.
Logistics Coordination:
4PLs utilize AI forecasting, TMS, WMS, IoT tracking, and control towers to centralize data, automate workflows, optimize routes, and provide real-time visibility. This minimizes delays, reduces errors, improves inventory accuracy, and increases end-to-end supply chain efficiency.
Technology Integration:
4PLs utilize advanced tools, including AI forecasting, TMS, WMS, IoT tracking, and supply chain control towers. These integrated systems combine data, automate operations, and reduce errors.
Advanced Support:
It provides:
- Limited real-time visibility into inventory, shipments, procurement, or production may hinder decision-making. A 4PL solves this problem by providing integrated dashboards, predictive warnings, and reporting.
- A 4PL offers regulatory expertise, customs assistance, and multi-carrier coordination to ease entry when entering a global or regional market.
- Companies that require AI, automation, robotics, or real-time tracking without investing in these technologies can rely on 4PLs to implement and manage them efficiently.
A 4PL becomes the single accountable entity for strategy, planning, technology, vendor management, and ongoing enhancement to provide a single, data-driven supply chain solution.
3PL vs 4PL: Detailed Comparison
Here are the details:
Scope and Service Responsibility
When evaluating the 4PL vs 3PL, the primary distinction lies in the scope of their services.
A 3PL has operations in transportation, warehousing, inventory, and order fulfillment. They manage specific tasks within a company’s supply chain.
But a 4PL maintains the entire logistics system. It collaborates with multiple 3PLs, carriers, and vendors to design supply chain strategies, optimize networks, and enhance end-to-end performance. This position calls the 4PL a strategic partner rather than an executor.
Asset ownership (3PL vs 4PL)
A significant 3pl vs 4pl difference is asset ownership.
3PLs often operate their own warehouses, vehicles, and fulfillment infrastructure, allowing companies direct access to existing logistics assets.
4PLs are usually non-assetless. Instead of owning trucks or facilities, they coordinate and manage assets across several logistics providers. This neutrality allows for greater flexibility, cost optimization, and a fair selection of vendors.
Communication and Client Relationship
In the 4PL vs. 3PL model, the communication style shifts from transactional to strategic.
The 3PL relationships are tactical – clients interact with the 3PL and its staff for timely information, warehouse coordination, or daily operational needs.
4PLs serve as a single point of contact for all supply chain activities. They connect, manage partners, provide predictive insights, integrate technology, and offer performance dashboards. The relationship is collaborative and long-term.
Use case suitability: Which logistics model fits your business?
Here is 3PL vs 4PL explained based on suitability:
A 3PL would be appropriate in cases where you require the effectiveness of execution, faster delivery, improved warehousing, or reliable shipping. This is ideal for small to mid-sized companies or brands that prioritize operational efficiency.
A 4PL is suitable for companies with a complex network of multiple vendors that require a high level of visibility, strategic planning, sophisticated analytics using AI, TMS, predictive tools, and international coordination. It is appropriate for businesses that want to optimise their supply chain, scale up, and have centralised control.
Comparison Table: 3PL Logistics vs 4PL Logistics
Companies can make informed decisions by acknowledging the 3PL vs 4PL differences.
| Feature | 3PL Logistics | 4PL Logistics |
| Primary Focus | Execution of specific logistics tasks like warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment | Strategic oversight and management of the entire supply chain |
| Scope of Service | Handles individual segments or tasks within the supply chain | Manages end-to-end supply chain, often integrating multiple 3PLs and carriers |
| Asset Ownership | Often owns physical assets such as warehouses, trucks, and equipment | Typically non-asset based; manages assets of 3PLs and other providers |
| Client Relationship | Transactional or tactical service provider | Strategic partner and single point of accountability |
| Level of Control | Client retains significant strategic control over logistics operations | Client delegates most operational control to the 4PL |
| Technology Use | Operational tools like WMS, inventory tracking, and shipping software | Advanced integration: AI, predictive analytics, TMS, WMS, IoT, and supply chain control towers |
| Key Objective | Cost reduction, operational efficiency, and faster fulfillment | Supply chain optimization, strategic alignment, and long-term value creation |
| Point of Contact | Client may manage multiple vendors or 3PLs | Single point of contact for all supply chain operations |
| Best For | Small to mid-sized businesses, e-commerce, retail, and straightforward logistics needs | Large enterprises, global supply chains, multi-vendor networks, and complex operations |
Pros & Cons of 3PL and 4PL Logistics
Understanding the 4PL vs 3PL can help companies select a model that meets their long-term requirements.
Pros of 3PL
3PLs provide businesses with operational efficiency, scalability, and access to technology without requiring heavy investments in infrastructure.
- Avoid capital expenditures on warehouses, fleet, employees, and logistics software; enjoy better shipping rates through 3PL volume discounts.
- Get expert experience in global compliance, import/export paperwork, and carrier administration.
- Businesses are freed from daily logistics management; instead, they can focus on manufacturing, selling, marketing, and expansion policies.
- Distributed warehouse networks can facilitate faster regional delivery and lower the cost of the last mile.
- Businesses utilize 3PL systems, including WMS, TMS, RFID, automated picking, and analytics, without requiring developer efforts.
- It provides Timely deliveries, correct order fulfillment, branded packaging, and streamlined returns, improving customer experience.
- 3PLs also offer brand-specific packaging, labels, and B2B/B2C fulfillment solutions.
Cons of 3PL
The 3PLs can bring some operational and dependency issues.
- Supervising daily picking, packing, routing, and warehouse operations is more difficult.
- The quality of service may vary depending on the warehouse staff’s ability and the provider’s SOPs.
- It involves integrating ERP systems with the provider’s WMS/TMS systems.
- Delays or network failures on the part of the provider may affect customer delivery.
Pros of 4PL
4PLs excel in end-to-end integration and strategic supply chain management.
- It acts like a long-term partner and always prioritizes the client’s supply chain goals.
- It maintains a high level of interactions with end customers to boost loyalty and satisfaction.
- It can optimize logistics, freeing resources for core business processes.
- It facilitates growth and market expansion through existing networks and industry relations.
- Act as a single point of contact to the entire supply chain, which allows enhanced visibility and efficiency.
Cons of 4PL
All businesses may not be fit with 4PLs.
- Depending on a single 4PL creates vulnerability. Any issues with the provider, such as service outages or financial difficulties, can disrupt your supply chain.
- The initial cost of 4PL services is higher. It requires high investment in integration and technology.
- It requires significant time, process redesign, data integration, and the establishment of governance.
- Building a 4PL alliance, which involves system integration, process alignment, and vendor onboarding, is a time-consuming and highly coordinated process.
How to Choose: 3PL vs 4PL
Selecting the suitable logistics provider involves identifying what you need, with 3pl vs 4pl explained clearly.
Business Needs:
The appropriate model depends on the company’s size and the complexity of its logistics.
3PL:
Best suited for small and medium-sized businesses or start-ups that require operational support for order processing, warehouse management, or last-mile delivery. 3PLs handle the day-to-day logistics. This enables the business to focus on the core issues of sales, marketing, and product growth.
4PL:
Appropriate for large enterprises or businesses with global supply chains and multi-vendor networks. 4PL providers deal with logistics on an end-to-end basis, encompassing several 3PLs, carriers, and IT solutions. This provides strategic control and operational efficiency.
Operational Costs & Budget:
The model is selected based on the company budget and logistics costs.
3PL:
Cost-effective because of easy logistics. You can pay only for services that you have used. Suited to companies having a small budget or seasonal demand fluctuations.
4PL:
Higher investment is required. But it offers long-term value through integrated management, advanced analytics, and process optimization, which minimizes operational redundancies.
Strategic Considerations:
Business goals and growth plans influence logistics strategy.
3PL:
Provides scalability and flexibility. This enables companies to rapidly scale their operations without compromising control over fundamental logistics.
4PL:
Focuses on strategic alliances, optimizing logistics to support the overall business objectives, enhancing supply chain efficiency, and increasing global visibility.
FAQs
- What’s the difference between 3PL and 4PL?
3PL handles specific logistics tasks, such as warehousing and transportation, while 4PL manages the entire supply chain, including multiple 3PLs, providing strategic oversight.
- Is 4PL better than 3PL?
Not always. 4PL is ideal for complex, global supply chains, whereas 3PL is cost-effective for simpler logistics needs.
- Can a 3PL act like a 4PL?
It may occur in some cases. 3PLs focus on execution, while 4PLs provide end-to-end strategic management.
- Which model suits growing e-commerce brands?
Most companies begin with 3PL for fulfillment efficiency, then transition to 4PL as their operations scale internationally.
Conclusion
If the goal is full supply chain transformation, a 4PL is typically the best option. Companies often begin with a 3PL and transition to a 4PL as their needs evolve, highlighting the key differences between 4PL and 3PL.







