Introduction
Warehouse logistics plays a pivotal role in modern supply chain management, serving as the backbone for efficient storage, movement, and distribution of goods. In Australia, with rapidly growing e-commerce and a complex supply chain network, the importance of warehouse logistics continues to intensify. Effective management in this area enables businesses to improve order accuracy, minimize costs, expedite shipping, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction. The Australian warehousing and logistics market is experiencing strong growth, projected at over 5% annually, driven by rising demand for faster delivery and technological innovation. This guide will explore the essentials of warehouse logistics, focusing on the unique attributes and challenges in the Australian market source.
What is Warehouse Logistics?
Warehouse logistics refers to the organized planning and control of the storage and movement of goods inside warehouses. It includes managing inventory, overseeing the picking and packing of orders, coordinating shipping schedules, and integrating inbound and outbound logistics activities. The objective is to optimize operational workflows to reduce handling errors and delays, leading to streamlined supply chains and better scalability. In Australia, where timely delivery impacts competitiveness, warehouse logistics integrates advanced software systems and automation technologies to maintain accuracy and efficiency at scale. For Australian businesses seeking optimized shipping processes, our detailed order fulfilment guide offers actionable insights.
Australia Warehouse Market Overview
The Australian warehouse logistics sector is a vibrant and growing market underpinned by increasing consumer demand and e-commerce penetration. Market research reveals that investments in warehousing infrastructure have surged, with companies like Linfox, Toll Group, and StarTrack leading innovations with large-scale distribution centers and advanced automation. These providers utilize technologies such as robotics and AI-driven warehouse management systems (WMS) to handle the complexities of inventory control and fulfillment with greater speed and accuracy. Additionally, strategic locations in states such as Victoria and New South Wales serve as logistics hubs supporting domestic distribution and international exports, especially to Asia-Pacific markets. This growth is supported by government initiatives that encourage supply chain resilience and technological upgrades sourcesource.
Types of Warehouses in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Understanding the diverse warehousing options is essential for selecting the right solution tailored to business needs. The major warehouse types include:
- Public Warehousing: These are third-party facilities offering flexible storage on a rental basis, suitable for businesses avoiding heavy capital investments. They provide scalability and shared services that accommodate fluctuating demands common in retail and seasonal industries.
- Private Warehousing: Owned and operated by a single company, private warehouses provide full control over operational procedures and inventory security, often preferred by large manufacturers and retailers with predictable volume.
- Bonded Warehousing: These specialized facilities secure imported goods under customs control, allowing deferred duty payments until goods are released for the Australian market. This option is crucial for importers managing cash flow and regulatory compliance.
- Smart Warehousing: Incorporating cutting-edge technology—like robotics, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs)—smart warehouses enable real-time inventory management and improve speed and accuracy. Australian warehouses adopting these technologies are setting new industry standards for productivity.
- Cold Storage Warehousing: For perishable goods like fresh produce and pharmaceuticals, these warehouses maintain controlled temperature environments that comply with strict Australian health standards.
- Distribution Centers: Focused on rapid sorting and redistribution, they serve as regional hubs that expedite deliveries to retailers and consumers, enhancing last-mile efficiency.
Exploring how Australian e-commerce businesses leverage these warehouse types can reveal best practice guidance for logistics success Ecommerce logistics.
Warehousing vs Storage in Logistics
While often used interchangeably, “warehousing” and “storage” have distinct meanings within logistics:
- Warehousing encompasses active logistics operations including receiving shipments, quality inspections, inventory management, order picking, packing, and shipping. It involves continuous movement and processing of goods aligned with demand patterns.
- Storage refers primarily to the passive holding of inventory over a period, without significant operational handling or processing.
In practical terms, warehousing incorporates storage but adds value through process optimization, ensuring products flow efficiently through the supply chain. Australian firms recognize this distinction in their logistics strategies, focusing heavily on warehousing to reduce order cycle times and enhance fulfillment accuracy. Comprehensive stocktaking to maintain inventory accuracy is another critical warehousing activity highlighted in our stocktake guide.
Advantages and Benefits of Warehousing in Logistics
Companies that invest in effective warehousing solutions reap multiple operational benefits:
- Improved Inventory Accuracy: Advanced tracking systems allow real-time visibility, which minimizes stock discrepancies, reduces stockouts, and avoids excess inventory holding costs.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimized storage layouts and mechanized handling reduce labor costs and operational waste, delivering significant cost savings in high-volume environments.
- Accelerated Order Fulfillment: Efficient picking and packing processes enable rapid dispatch, critical in Australia’s vast geography where timely delivery drives customer loyalty.
- Customer Satisfaction: Accurate orders and reliable, predictable delivery build brand trust in competitive markets.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Warehousing adapts to demand fluctuations and seasonal spikes, supporting business growth without the constraints of fixed capacity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Specialized warehouses comply with Australian standards for temperature-controlled goods, hazardous materials handling, and customs regulations.
For maximizing these benefits, pairing warehousing solutions with a reliable shipping partner ensures cohesive supply chain performance.
Difference Between Logistics and Warehouse
In simplest terms:
| Aspect | Warehouse | Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical facility for storing goods | Management of product flow across the entire supply chain |
| Scope | Storage and order processing inside facility | Comprehensive flow including transport, storage, and delivery |
| Focus | Inventory control and fulfillment | Coordinated supply chain network management |
| Activities | Receiving, storing, packing | Transportation, warehousing, inventory control, delivery |
| Objective | Safekeeping and efficient handling | Delivering goods to customers cost-effectively and timely |
Understanding this difference is vital to optimizing warehouse investment and integrating it into a broader logistics strategy aimed at meeting Australian customer expectations source.
Best Practices for Efficient Warehouse Logistics
Australian warehouses employ several proven approaches to optimize performance:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Automate inventory tracking, order processing, and reporting to minimize errors and provide actionable data.
- Automation and Robotics: Use technology like robotic picking and automated conveyor belts to speed up operations and reduce manual labor risks.
- Staff Training: Ongoing training programs keep employees updated on technology use, safety protocols, and process improvements.
- Warehouse Layout Optimization: Smart design ensures smooth flow, minimizes travel time for pickers, and allows safe movement of materials.
- Supply Chain Integration: Seamless data exchange with suppliers and transportation partners enhances coordination, reduces delays, and ensures stock availability.
Detailed integration solutions that support Australian e-commerce providers are reviewed in our ecommerce logistics integration guide.
Future Trends in Warehouse Logistics Australia
Technological, environmental, and strategic trends are shaping the future of Australian warehouse logistics:
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Tools that forecast demand patterns and optimize stock levels are becoming mainstream.
- IoT for Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors track inventory status, temperature, and equipment performance, alerting managers to issues proactively.
- Sustainability Practices: Adoption of green technologies including solar power, energy-efficient lighting, and recyclable building materials reduces carbon footprints.
- Collaborative Models: Sharing warehouse and transport resources across businesses improves asset utilization and cost sharing.
- Emerging Technologies: Voice-directed picking, augmented reality, and blockchain for secure transaction tracking are on the horizon.
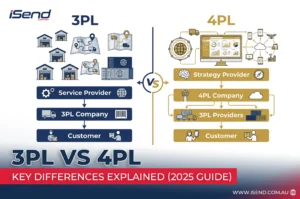
3PL and 4PL Warehousing in Australia
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer flexible, scalable warehousing solutions critical to Australian SMEs and large enterprises alike. These providers handle inventory management, order fulfillment, and returns management at competitive rates, often benefiting from economies of scale and superior technology. Fourth-party logistics (4PL) providers take this a step further by managing and integrating entire supply chains, optimizing multiple logistics components for end-to-end visibility and cost savings. Typical 3PL warehousing costs range AUD 8-15 per pallet per week depending on services and contract length. More on 3PL solutions for Australian ecommerce businesses can be found 3pl logistics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How much does warehousing cost in Australia?
Costs vary based on warehouse type, location, and service scope, typically AUD 8-15 per pallet weekly. Climate control and value-added services may increase fees.
Q2: What are the common types of warehouses in Australia?
Public, private, bonded, smart, cold storage, and distribution centers serve various industries and regulatory requirements.
Q3: Which warehouse management technologies are popular in Australia?
WMS, robotics, IoT sensors, and automation systems are widely adopted to improve operational accuracy and efficiency.
Q4: Should I outsource warehousing through a 3PL provider?
For many Australian businesses, 3PLs offer cost savings, operational expertise, and scalability without capital investment.
Q5: What workplace health and safety rules apply to warehouses in Australia?
WHS regulations require safety training, proper equipment handling, and ergonomic workstations to prevent injuries and ensure compliance.
Q6: How important is sustainability in Australian warehousing?
Increasingly important, sustainability initiatives reduce costs and carbon footprints, complying with national environmental targets.
Conclusion
Warehouse logistics forms the backbone of Australia’s supply chains, enabling businesses to meet growing consumer demands with speed and accuracy. Selecting appropriate warehouse types, investing in automation and technology, adhering to best practices, and partnering with reliable logistics providers are essential strategies for success. Staying informed on future trends and regulatory shifts will ensure businesses remain competitive in Australia’s dynamic market.
Develop your logistics strategy with our detailed shipping policy guide.